This document describes the main features of MatrixGate.
Notes!
Programming Language Access MatrixGate Please see Data Write - Programming Language Access MatrixGate.
csvtable in the demo database.demo=# CREATE TABLE csvtable (
time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE,
tagid INT,
c1 INT,
c2 INT,
c3 INT
)
USING MARS3
DISTRIBUTED BY (tagid)
ORDER BY (time,tagid);1603777821|1|101|201|301
1603777822|2|102|202|302
1603777823|3|103|203|303--source parameter is stdin, the target table is the existing csvtable, and the loading parallelism is 2. In the example, the host is mdw.[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate \
--source stdin \
--db-database demo \
--db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \
--db-master-port 5432 \
--db-user mxadmin \
--time-format unix-second \
--delimiter "|" \
--target csvtable \
--parallel 2 < data.csvdemo=# SELECT * FROM csvtable ;
time | tagid | c1 | c2 | c3
-----------------------+-------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2020-10-27 05:50:23+08 | 3 | 103 | 203 | 303
2020-10-27 05:50:22+08 | 2 | 102 | 202 | 302
2020-10-27 05:50:21+08 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 301
(3 rows)demo=# CREATE TABLE json_test(
id int,
j json
)
USING MARS3
ORDER BY (id);~/json.csv.
1|"{""a"":10, ""b"":""xyz""}"--format csv.[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate \
--source stdin \
--db-database postgres \
--db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \
--db-master-port 7000 \
--db-user mxadmin \
--time-format raw \
--format csv \
--delimiter "|" \
--target json_test < ~/json.csvdemo=# SELECT * FROM json_test;
id | j
----+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {"a":10, "b":"xyz"}
(1 row)demo=# CREATE TABLE json_array_test(
id int,
j json
)
USING MARS3
ORDER BY (id);~/json_array.csv.1|"{""{\""a\"":10, \""b\"":\""xyz\""}"",""{\""c\"": 10}""}"[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate \
--source stdin \
--db-database postgres \
--db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \
--db-master-port 7000 \
--db-user mxadmin \
--time-format raw \
--format csv \
--delimiter "|" \
--target json_array_test < ~/json_array.csvdemo=# SELECT * FROM json_array_test ;
id | j
----+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {"{\"a\":10, \"b\":\"xyz\"}","{\"c\": 10}"}
(1 row)Notes!
Because the JSON column contains special characters such as quotes, the --format parameter of mxgate must be CSV.
watch is a subcommand of mxgate that uses a series of indicators to describe the operation of mxgate daemon.
There are two modes of watch:
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate watchThe running indicators of mxgate will be collected every three seconds, and the output results are as follows
Time WCount ICount WSpeed/s ISpeed/s WBandWidth MB/S BlocakItems
2022-04-28 15:20:58 14478858 14527011 2598081 2627887 2395 0
2022-04-28 15:21:01 22231035 22633254 2584059 2702081 2222 0
2022-04-28 15:21:04 30494310 30500874 2754425 2622540 3551 0
2022-04-28 15:21:07 38004210 38032956 2503300 2510694 2862 0
2022-04-28 15:21:10 46188696 46298223 2728162 2755089 2227 0
...The description of each indicator above can be obtained through the --info parameter
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate watch --infoBy default, only speed indicators will be output, and the time indicator can be observed through the --watch-lateency parameter to analyze problems.
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate watch --watch-latency[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate watch --historyThe average speed per hour in 24 hours as of the current time will be calculated, and the output result is as follows
TIME RANGE | SPEED/S | BANDWIDTH MB/S | BLOCK ITEMS
2022-04-28 16:00:00-2022-04-28 17:00:00 | 2208010 | 1254.48 | 0
2022-04-28 17:00:00-2022-04-28 18:00:00 | 1157920 | 1327.00 | 0
2022-04-28 18:00:00-2022-04-28 19:00:00 | 2228666 | 2162.32 | 0
2022-04-28 19:00:00-2022-04-28 20:00:00 | 1371092 | 2881.30 | 0
2022-04-28 20:00:00-2022-04-28 21:00:00 | 1575320 | 2608.20 | 0Among them, SPEED/S, BANDWIDTH MB/S represents the imported entry speed and import bandwidth (MB/s in units), BLOCK ITEMS represents the amount of data blocking in mxgate. This value will rise when the database consumption speed cannot keep up with the production speed of data sources (http, kafka, etc.).
You can add --watch-start, --watch-end, --watch-duration parameters to control the time interval and period of observation historical data.
For example
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxgate watch --history --watch-start '2022-03-27 00:00:00' --watch-end '2022-04-27 00:00:00' --watch-duration '168h'Average import speeds per week (every 168h) from March 27 to April 27
Among them, --watch-duration supports three units: h``m``s
mxgate supports modifying parallel loading parameters --stream-prepared and --interval without stopping the run:
--stream-prepared represents the number of active slots when mxgate writes data to each table of YMatrix. By default, the number of slots in all tables is the same. It can be manually adjusted for a single task (Job) (only one task per table).--stream-prepared value often means improving the concurrency of data writing, thereby improving performance, and also occupies more memory resources.--stream-prepared value can reduce the use of memory resources of the data node (Segment), but the performance will also be reduced accordingly.--interval represents the working interval time of each active slot, that is, after each slot waits for --interval (in milliseconds, ms), the data received by mxgate during that period is sent to YMatrix.--interval means that the delay of each slot will increase every time the data is written, and the amount of data written will increase (provided that data is continuously flowing into mxgate).--interval, and the delay is reduced and the amount of data is also reduced.In summary, in production practice, the above two parameters need to be reasonably adjusted in conjunction with different storage engines and users' requirements for real-time data writing.
Specific usage examples are as follows:
$ mxgate set --stream-prepared-cli 3$ mxgate get --stream-prepared-get$ mxgate set --job-interval 200
$ mxgate get --job-interval-getNotes!
For the above parameters, if you want to set or get the slot number or working time of a specific table, then add--job <name>after the above command. Each task corresponds to a database table. The job parameter structure consists of a schema name and a table name, which means that if your specific table is called test_table and the schema name is public, then you need to add--job public.test_tableafter the existing command.
During data loading, as time-series data sources become more and more abundant, the table structure set previously may no longer be applicable to the current scenario, so there is a need to modify the table structure. This section will explain how mxgate pauses data writing, reloads table meta information, and restores data writing without shutting down. The specific steps are as follows:
mxgate pause -X to interrupt the slot of all tables to prepare for modifying the database table structure. Where the -X parameter is necessary, it will help interrupt the slot between mxgate and the database. If slot is not interrupted, the database table cannot be modified. In addition to -X, the -S parameter can be used to make the pause mission synchronously wait for all slot interrupts to complete before returning.$ mxgate pause -X
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
begin to pause all jobs,please wait...Notes!
The reconstructed table structure can be different, but the "table name" must be consistent.
mxgate resume -R to restore slots of all tables and overload meta information of the data table. Where the -R parameter is required, resume and -R will combine to complete the reload operation.$ mxgate resume -R
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
begin to reload all jobs,please wait...-p parameter is required to represent the process number of the corresponding mxgate process. All the above commands are the same, for example:$ mxgate get --job-interval-get -p 70199 --jobNotes!
The prerequisite for executing the overloaded command is that all slots in the corresponding table of mxgate must be paused first, otherwise an error will occur:jobs are not paused, please pause them first
Notes!
If the pause action timeout (50 seconds), the insertion operation of the corresponding Slot is cancelled to ensure that the pause operation can be completed normally.
YMatrix implements the UPSERT function of MatrixGate from v4.2.0. For details, see Data Batch Merge Scenario (UPSERT).
YMatrix implements MatrixGate's single table migration function from v4.3.0. For details, see Single Table Migration.
Notes!
YMatrix not only supports single table migration, but also supports full library migration (v4.7.0 and above). For details, see Full Library Migration.
Sometimes we need to turn on the debug log of mxgate to observe some key information, but turning on or off the debug log requires restarting mxgate, which is not conducive to positioning problems. Therefore, YMatrix provides the ability to dynamically change the mxgate log level:
mxgate set --log-level VERBOSE to enable the VERBOSE level log with relatively complete information or mxgate set --log-level DEBUG to enable the DEBUG level log with the most complete information. When you do not need to observe the debug log, you can use mxgate set --log-level INFO to restore the log level to INFO.Sometimes we need to make some DDL modifications to a table during the insertion operation by mxgate. This function allows mxgate to "back" the incoming insertion operation after receiving the DDL modification instruction, so that the DDL statement can be executed as soon as possible.
Supported DDL operations are as follows:
=# TRUNCATE TABLE <tablename>;=# ALTER TABLE <tablename> ADD COLUMN <columnname> <columndatatype>;
=# ALTER TABLE <tablename> DROP COLUMN <columnname>;
=# ALTER TABLE <tablename> ALTER COLUMN <columnname> TYPE <columndatatype>;=# ALTER TABLE <tablename> RENAME TO <new tablename>;=# DROP TABLE <tablename>;
=# CREATE TABLE <tablename(column datatype)>;Typically, we can adapt the load (i.e. the amount of data to be written) of different write tasks by manually adjusting stream-prepared parameter (the number of slot sessions executed in parallel). However, in some business scenarios, there are continuous dynamic changes in the load of the write task, and this change cannot be adjusted manually.
Therefore, MatrixGate designed an automatic mechanism: automatic adaptation of the write load is completed by turning on the --auto-tune parameter.
This parameter can be enabled in the following ways:
Notes!
Turning on this function can ensure the most efficient write performance in real time, but the utilization of session slot resources is not necessarily optimal.
Notes!
If you set the automatic adjustment of slot number on and also set the [High Water Threshold] (#sourcepressure), the automatic adjustment of slot number function will only take effect if the write load exceeds the threshold.
mxgate supports quantification of the write load of the source data (percentage 0 to 100%). During the process of mxgate writing data, the write load of the corresponding task (Job) can be obtained through the following command:
$ mxgate get --source-pressure
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
public.t2 source-pressure = 27.26%If there are multiple jobs, you can get the corresponding write load through the name of the job, or get the write load of multiple jobs at once:
$ mxgate get --source-pressure --job public.t2
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
public.t2 source-pressure = 15.73%$ mxgate get --source-pressure
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
public.t2 source-pressure = 35.84%
public.t1 source-pressure = 0%After completing the percentage load quantization, you can use this metric to set a corresponding high water level threshold. If the data writing load at the source end exceeds the set threshold, the corresponding number will be displayed as red. At this time, you can manually adjust the slot number to reduce the write pressure. Of course, you can also use the [mxgate automatic slot number] (#autotune) function.
The threshold value needs to be set through the following command:
$ mxgate set --high-water-mark <highwatermark> --job <jobname>For example:
$ mxgate set --high-water-mark 20 --job public.t2
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
public.t2 high-water-mark = 20.00%Get the high water level threshold of the corresponding job through the following command:
$ mxgate get --high-water-mark-get --job public.t2
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
public.t2 high-water-mark = 20.00%$ mxgate get --high-water-mark-get
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
public.t1 high-water-mark = 0.00%
public.t2 high-water-mark = 20.00%Notes!
If the set threshold value is exceeded, the pressure value will turn red.
If you enable the automatic adjustment slot number function of mxgate and set the corresponding high water level threshold, then the slot number will not automatically increase until the loading pressure value of the job does not exceed the set high water level threshold, and it will be useless even if mxgate attempts to increase through the automatic adjustment function**.
For example: We set a high water threshold of 75%. When the loading pressure is 35%, although mxgate judged that the number of slots should be increased, because the 75% of the high water level threshold setting is not reached, the number of slots will not increase at this time, but will display the following error:
[WARN]:-[SlotsLauncher] Sources pressure = 35.21 of job(public.t2) is lower than the high water mark(75), the slot increase is not allowedNotes!
The example values are for reference only. Please set the corresponding high water level threshold based on actual business needs and current data writing speed.
If you want to remove the limit of the high water level threshold, you can use the following command:
$ mxgate set --disable-high-water-mark=true --job public.t2
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: v5.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2023-10-26; any
**********************************************************
public.t2 high-water-mark = 0.00%You can view all mxgate processes that are currently writing data to the YMatrix database or have completed writing data by querying the matrixgate_internal.mxgate_process_view view in the matrixmgr database.
matrixmgr=# SELECT * from matrixgate_internal.mxgate_process_view;
id | pid | host | port | source | database | external_table_schema | has_metrics | created_at | exited_at | exited | schema_cleaned | mxgate_config | updated_at
----+---------+------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
13 | 63431 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_63431_sdw2_b7b30959 | t | 2024-04-03 16:45:27.789389+08 | 2024-04-03 16:45:27.981513+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 10} |
14 | 66038 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_66038_sdw2_e810e04d | t | 2024-04-03 16:45:54.381101+08 | 2024-04-03 16:45:54.571016+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
15 | 98535 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_98535_sdw2_b5032eff | f | 2024-04-03 16:49:50.540095+08 | 2024-04-03 16:49:50.753405+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
16 | 102059 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_102059_sdw2_c0f9dbc4 | f | 2024-04-03 16:50:30.544932+08 | 2024-04-03 16:50:30.749403+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
17 | 104761 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_104761_sdw2_f284b2f2 | t | 2024-04-03 16:50:40.909025+08 | 2024-04-03 16:50:41.10522+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 10} |
18 | 105109 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_105109_sdw2_9ffa1360 | f | 2024-04-03 16:50:42.324334+08 | 2024-04-03 16:50:42.501187+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
19 | 110590 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_110590_sdw2_527394f9 | f | 2024-04-03 16:51:28.265894+08 | 2024-04-03 16:51:28.468763+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 0} |
20 | 110760 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_110760_sdw2_c7d787a3 | t | 2024-04-03 16:51:29.730855+08 | 2024-04-03 16:51:29.957642+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 10} |
21 | 110882 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_110882_sdw2_6bdbd471 | f | 2024-04-03 16:51:31.189347+08 | 2024-04-03 16:51:31.383211+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
22 | 112484 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_112484_sdw2_83dc4c87 | f | 2024-04-03 16:51:47.735186+08 | 2024-04-03 16:51:47.943989+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 0} |
23 | 112608 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_112608_sdw2_ebd6fcb1 | t | 2024-04-03 16:51:49.202759+08 | 2024-04-03 16:51:49.413013+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 10} |
24 | 112746 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_112746_sdw2_804d4e9c | f | 2024-04-03 16:51:50.651448+08 | 2024-04-03 16:51:50.82829+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
25 | 114206 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_114206_sdw2_1376e4f0 | f | 2024-04-03 16:52:05.954983+08 | 2024-04-03 16:52:06.150763+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 0} |
26 | 114323 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_114323_sdw2_31f5fe71 | t | 2024-04-03 16:52:07.392493+08 | 2024-04-03 16:52:07.606231+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 10} |
27 | 114454 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_114454_sdw2_84a2439d | f | 2024-04-03 16:52:08.849134+08 | 2024-04-03 16:52:09.044388+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
28 | 118611 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_118611_sdw2_11aa241a | f | 2024-04-03 16:54:08.596567+08 | 2024-04-03 16:54:08.806036+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 0} |
29 | 118754 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_118754_sdw2_9c835dfc | t | 2024-04-03 16:54:10.04123+08 | 2024-04-03 16:54:10.28288+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 10} |
30 | 118879 | sdw2 | 8891 | http | kafka_gate_json | _matrixgate_118879_sdw2_d58b7ed2 | f | 2024-04-03 16:54:11.521661+08 | 2024-04-03 16:54:11.72412+08 | t | f | {"metrics_interval": 15} |
(18 rows)Or check it through the following command.
$ mxgate get mxgate-process-info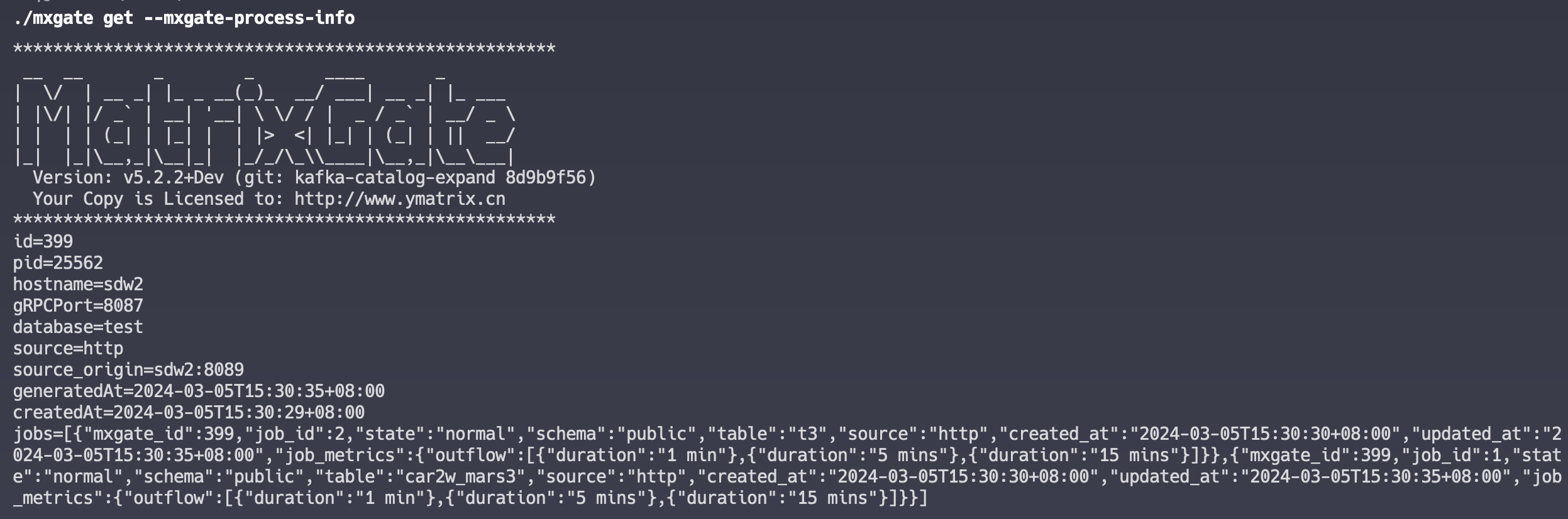
Parameter description:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| id | self-increase ID |
| pid | mxgate process PID |
| host | mxgate server hostname |
| port | mxgate The port number of the gRPC service exposed to the outside |
| created_at | mxgate The time when the process was created. After the process starts, the time will not be updated again |
| exited | mxgate Whether the process is exited. Under normal circumstances, when the mxgate process is running, the parameter value is false; the mxgate process exits normally. If the Control + C or mxgate stop command is executed, the parameter value is true; if the mxgate process exits abnormally (such as manually killed or the server is offline), it may cause mxgate to not have time to modify this value when exiting, and it will remain in the false state |
| cleaned | Whether the external table schema used by the mxgate process has been deleted. If the mxgate process is running, the parameter is false; if the mxgate process exits normally, the parameter will become true in a few seconds; if it exits abnormally, it may cause mxgate to not have time to modify this value when exiting, so the relevant mode cannot be deleted immediately, and it will remain in the false state. To cope with this situation, YMatrix internally maintains the mxgate heartbeat time. If the heartbeat is not updated after 2h, it is considered that the mxgate process has exited, the relevant external table pattern will be deleted, and the parameter will become true |
| database | mxgate connected database |
| source | mxgate's data source type (HTTP / Stdin / Kafka / Transfer) |
| updated_at | mxgate The mxgate process updates this time every 3 seconds. This time is the update time of the mxgate process on YMatrix Master. If the mxgate process exits normally, the updated_at parameter of the corresponding id queryed in the matrixgate_internal.mxgate_process_view view will become NULL |
| has_metrics | mxgate Whether the module that collects various data statistics and performance indicators internally is started. When this field is false, the return result of the mxgate get mxgate-process-info command is empty |
| external_table_schema | Records the schema of the external table created by mxgate. Used to clear the residual mode after mxgate exits abnormally |
| mxgate_config | Used to save key fields in the mxgate config file, so that after the mxgate process exits, you can still check the corresponding configuration information (v5.3.2 starts to support) |
Currently, all types of mxgate data sources (Stdin, HTTP, gRPC, Transfer) support information statistics for data insertion into system tables and error logs. in:
INSERT operation (success/partially successful/failed);View the insert system table by following the following command:
=# SELECT * FROM matrixgate_internal.insert_catalog;
id | mxgate_id | insert_sequence | slot_id | session_id | created_at | status | source | flows_cnt | total_lines | bytes_length | target_table | message | job_id
----+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 | 39 | 1 | 10 | 152832 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | partial | http | 10 | 100 | 600 | "public"."concurrent_insert_error_log_varification_http_source" | 20 malformed messages | 1
(1 row)Parameter description:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| id | self-increase ID |
| mxgate_id | mxgate Process ID. Corresponding to the id field in the mxgate_process_view view |
| insert_sequence | The serial number of this insert operation, slot will be added to 1 for every insert |
| slot_id | The ID number of slot corresponding to this insert |
| session_id | This insert, mxgate is the session ID for establishing a connection between the client and the database |
| created_at | The creation time of this insert record |
| status | The status of this insert includes: success / partial / fail (success/partial success/fail) |
| source | mxgate Data source type |
| flows_cnt | How many batches does this insert contain |
| total_lines | How many lines are there in this insert |
| bytes_length | How many bytes of data does this insert contain in total |
| target_table | Target table for data writing |
| message | If a write error occurs, it indicates the cause of the error |
| job_id | The ID of the job is in the form: "schema"."table" |
View the error log table with the following command:
=# SELECT * FROM matrixgate_internal.insert_error_log;
catalog_id | created_at | received_at | line_number | errmsg | rawdata
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 6 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c5
3 | 2024-03-15 13:17:32+08 | 2024-03-15 13:17:31+08 | 9 | invalid input syntax for type integer: "error", column id | error|c8
(20 rows)Parameter description:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| catalog_id | Self-increment ID. The corresponding id field of the system table is inserted |
| created_at | The time when this record was created |
| received_at | Time when this data was received by mxgate |
| line_number | line number of this data |
| errmsg | Cause of error |
| rawdata | raw data |
Note!
mxgate If you encounter a situation where the entire batch of data in a write operation fails, you will only record astatus = failinformation in thematrixgate_internal.insert_catalogtable, and will not record the error tuple of each row in thematrixgate_internal.insert_error_logtable.